Chapter-11
Urinary System
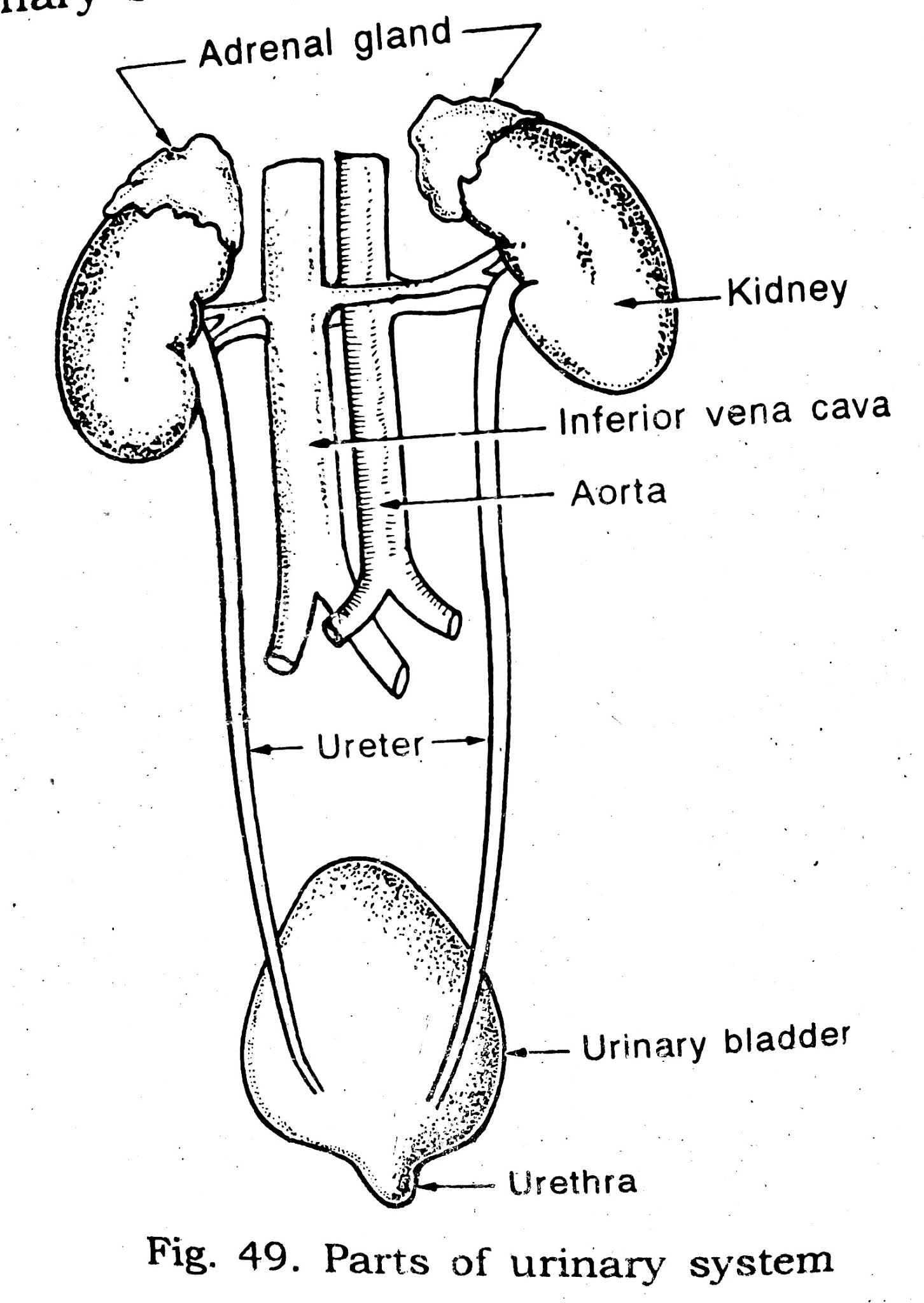
The urinary system is the main excretory system of the body. It consists of
1) two kidneys
2) two ureters
3) an urinary bladder
4) an urethra.
Kidney:
Mesodermal in origin.
Right kidney slightly lower than the left kidney due to presence of liver on right hand side.
They are two bean shaped organs lying on the posterior abdominal wall, on each side of the vertebral column.
External structure of kidney
1. Reddish brown in colour
2. Bean shaped
3. 11cm×5cm×3cm dimension
4. 150gm in weight each kidney
5. Consists of hilum through which renal artery enter and renal vein and ureter leaves from kidney
6. Outer border is convex, inner border is concave which contain hilum.
Internal structure of kidney
1. An outer cortex which is reddish- brown in colour.
2. Inner medulla which contains pyramids of the kidney.
3. An upper expanded end of ureter called pelvis.
4. There are several pyramids which drain urine to minor calyx. The 4to 5 minor calyx drain urine to major calyx. Then renal pelvis and lastly through ureters
Functions of the kidneys:
1. Excretion of water and waste products of protein metabolism.
2. Excretion of excess salt.
3. Excretion of harmful substances, drugs and toxins.
4. Regulation of pH of blood.
Nephron
Microscopically the kidneys are made of a number of structural and functional units called nephrons. There are about one million nephrons in each kidney. A nephron consists of two parts:
1. Malphigian bodies made of Bowman's capsule and glomerulus.
2. Renal tubules.
Malphigian bodies: It is made of 1) an upper expanded end of the renal tubule called Bowman's capsule 2) a bunch of capillaries called glomerulus which are packed in Bowman's capsule. The malphigian bodies are present in the cortex.
Renal tubules: They consist of four parts:
1. Proximal convoluted tubule situated in the cortex.
2. Loop of Henle present in the medulla.
3. Distal convoluted tubule present in the cortex.
4. Collecting tubules which pass through the medulla and open into the pelvis of kidney.
FORMATION OF URINE:
The formation of urine by kidney involves three process
1. Glomerular filtration
2. Tubular secretion
3. Tubular reabsorption
1. Glomerular filtration: Filtration of water, salts and other substances occurs in the glomeruli. Glomerular filtrate is the fluid that is formed after filtration. About 100 ml of glomerular filtrate is formed per minute. This filtrate passes into the proximal convoluted tubule.
2. Tubular secretion: It is an active process which occurs in the convoluted tubules. Abnormal substances or normal substances present in excess in blood are eliminated by this process. Potassium, hydrogen and drugs like penicillin are excreted by tubular secretion.
3. Tubular reabsorption: The rate of glomerular filtration is about 100 ml per minute. So about 6 litres of glomerular filtrate can be formed in one hour. But the volume of urine eliminated per day is only about 1.5 litres. It is so, because nearly 99 percent of the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed. Reabsorption of water occurs in the convoluted tubules and collecting tubule. addition to water, some salts are also reabsorbed in the renal tubules.
Urine is the fluid that results from the above three processes. It enters the collecting tubules and then into the pelvis of kidney. From there, it enters the urinary bladder through ureter.
URETER:
It is the duct which carries urine from the kidney to bladder. It is a tube like structure measuring about 26 cm in length. It commences from the pelvis of kidney. Later it passes down in the abdominal cavity and opens in the posterior aspect of urinary bladder. Ureter is made of
1) an outer fibrous layer
2) middle muscular layer
3) inner mucous layer.
URINARY BLADDER:
Present in pelvis. Made up of three layer as same of ureters. Highly dentisible due to presence of detrussor muscle. Bladder has three openings, two for ureters and one for urethra. The triangular area between these openings is the trigone of the bladder. Capacity in male 300 to 500ml and in female 700 to 800ml
URETHRA:
It is a canal through which urine passes from the bladder to the outside. It differs in the males and females. But a sphincter is present in both.
Male urethra: It is about 20cm in length. It consists of three parts
1) Pelvic part 2.5 cm
2) Perineal part 2.5cm
3) Pineal part. 15cm
Female urethra: It is short and measures about 4 cm in length. It starts from the base of bladder at the trigone. It opens externally in front of vaginal opening.
















































Comments
Post a Comment